
March 31st is World Backup Day, an annual date celebrated by the tech industry to highlight the importance of protecting your data and keeping your systems secure. Yet, many businesses don’t have backup and recovery solutions in place for their critical business data.
It is common for organizations to invest in preventative cybersecurity defenses. In fact, most organizations have technologies such as firewalls and anti-virus software that are designed to stop a cyber-attack.
These controls certainly serve a purpose in fighting the war against cybercrime and should not be discounted but the reality is, defending your business from cyber-attacks is an incredibly hard task to do.
Hackers are anonymous, perimeters are not physical, attacks are sophisticated, and the volume of cyber assaults launched every day is astounding. Defending cyber-attacks is a little like entering a cage fight blindfolded with one arm tied behind your back.
Despite the best defensive efforts, you will get hit.
If you do not regularly backup critical data and systems, then you must start doing so immediately.
With Datto, your company can be up and running in just seconds after a disaster.
Instant virtualization combined with the ability to backup as frequently as every 5 minutes means that with the click of a button, your Datto device recreates your computers and servers so your business can resume as if nothing had ever happened.
Our Datto devices utilize a reliable data backup redundancy solution by storing your critical business data onto your local Datto device as well as 2 offsite cloud storages. Datto even includes ransomware detection by running analytics to compare the two most recent backup snapshots to identify ransomware footprints.
Have you updated your backup process for today’s threats? Contact us today at 716-373-4467 x115 or [email protected] to schedule a chat about data backup and protection.
You can also visit our website here to learn more about our data backup and recovery solutions.
Read More

There are many things that have changed since the invention of the internet. One of these is how we bank and access our accounts. You used to have to go into a local bank branch to make deposits and withdrawals. Now, you can take a picture of a check and deposit it from your phone.
Approximately 73% of people around the world use some form of online banking at least once a month. People have never had such convenient account access. But that convenience can come at a cost.
In 2021, account takeover fraud increased by 90%. New account fraud jumped a whopping 109%. As the ease of online banking has increased, so has banking-related cybercrime.
If someone breaches your Facebook account, it can be a real pain. But, if a hacker breaches your bank account, it can be devastating. It can mean significant losses. Losses that you may not be able to recoup from your financial institution.
In this article, we’ll take a look at the mistakes people make that leave their accounts at risk. Then, we’ll go over some important tips on how to keep your bank account better protected.
Mistakes That Allow Criminals to Access Your Account
Not Enabling Two-factor Authentication
Two-factor authentication (2FA) is a simple process that packs a big punch. When you enable this setting in an online account, it requires an extra step to gain access. That step usually consists of receiving a one-time passcode (OTP) by SMS and entering that at login.
Many people make the mistake of leaving this disabled. They either don’t know it’s there or they think it’s too inconvenient. But leaving this setting off makes it much easier for a bad actor to breach your account.
If you’ve ever had a company inform you that it’s had a data breach, it’s likely your details could be floating around the dark web. If that’s the case, it’s only a matter of time until you’re targeted by cyber criminals. Reach out to us today to learn more about our Dark Web monitoring services.
Falling for a Phishing Scam
There are several types of phishing scams that target online banking. Cyber criminals send emails that look like they come from your bank. They’ll even promise incredibly low rates on credit cards.
Other scams can involve warning you of unauthorized account activity. But when you click the link to log in, you’re actually on a fake page. One designed to look just like your normal bank website.
These are just a few ways that scammers can get your online banking login details. Once they have them, they’ll act immediately to get whatever they can.
Using Easy-to-Guess Passwords
If your account password is easy to remember, it’s also often easy to guess. Using weak passwords is a common mistake that enables many cyber criminals.
Some best practices for passwords include:
- Make them at least 10 characters long
- Include at least one number
- Include at least one symbol
- Include at least one upper-case letter
- Don’t make them personal (e.g., don’t use your birthdate, etc.)
Downloading Unsafe Mobile Apps
Banking trojans are often hidden in malicious mobile apps. These apps can look like something as innocent as a task manager. But, once installed, banking trojans seek out any details they can find. They are looking for banking and wallet apps.
Logging Into Online Banking While on Public Wi-Fi
One surefire way to give away your online banking password is to log in while on public Wi-Fi. Hackers hang out on public hot spots and spy on the activity of others. You should never type in a password or other sensitive details when connected to public Wi-Fi.
Tips for Improving Online Banking Security
Turn On Two-Factor Authentication
Enable two-factor authentication in your online banking account. This is also known as multi-factor authentication or two-step verification. According to Microsoft, it can block 99.9% of fraudulent account login attempts.
Click here to read more about multi-factor authentication and the benefits it provides. Contact Databranch today for assistance with implementing this highly effective security measure for your business.
Set Up Banking Alerts
Time is of the essence when an intruder breaches your account. The faster you can notify your bank of the breach, the better. You could reduce the impact on you by having your account locked down immediately.
Set up banking alerts through your online banking. These can include things like low-balance alerts and login alerts.
Install an Antivirus & DNS Filtering On Your PC
It’s important to have reliable antivirus software on your PC. Many people don’t think about protecting their personal devices in the same manor as their company devices. Yet, they shop online and bank via laptops almost daily.
It’s also good to use a DNS filter. This is a filter that protects you from going to dangerous phishing sites by blocking them.
In search of a good antivirus for your company devices? Contact Databranch today to discuss our full endpoint protection software that will protect your employees against viruses, malware, ransomware, phishing and other cyber-attacks.
Take Phishing Training Classes
Do you know how to identify phishing? Are you up on all the newest scams? You can make yourself less vulnerable by taking our Cybersecurity Awareness Training. Knowing how to spot phishing via text, email, and phone can help you avoid becoming the next victim.
Our Cybersecurity Training Courses for 2023 is available now! Contact Databranch today for more information on these courses or how you can enroll in our Breach Prevention Platform and Security Awareness Training with simulated phishing tests.
Get Help Protecting Your Business from Scams
There are some key digital solutions we can put in place to keep your business safer from online threats. Contact us today at at 716-373-4467 x115 or [email protected] to schedule a chat about online security.
Article used with permission from The Technology Press.
Read More
Upcoming Changes to Microsoft Office 365 Authenticator App
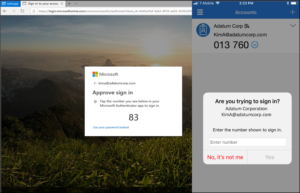
Microsoft has announced an upcoming change to the default method used in its Authenticator App. Starting May 8th, 2023, users will be required to input a verification number into the authenticator app. This date was previously February 27th, but Microsoft recently released a revision to the start date.
This number matching method is replacing the approve/deny push notification sent to mobile devices. Number matching is a key security upgrade to traditional second factor notifications in Microsoft Authenticator.
Microsoft will remove the admin controls and enforce the number match experience tenant-wide for all users starting May 8th, 2023.
Please note that this change will occur for both PCs and mobile devices. No action is required by the end users, this change will happen automatically by Microsoft.
If you have any questions regarding this upcoming change, or need any assistance, please contact Databranch Service at 716-373-4467 x4.
Microsoft Office 365 Changes to Security Defaults
Security Defaults are the preconfigured security settings that exist on your Microsoft accounts. Microsoft has announced that throughout the spring and summer of 2023, they will be rolling out Azure AD Security Defaults to all existing tenants.
Some of the changes enforced by the Security Defaults are below:
- Requiring all users and admins to register for MFA using the Microsoft Authenticator app.
- Challenging users with MFA, mostly when they show up on a new device or app, but more often for critical roles and tasks.
- Disabling authentication from legacy authentication clients that can’t do MFA.
- Protecting admins by requiring extra authentication every time they sign in.
Things to watch for:
- Automated emails/Reports from applications and vendors
- Scan to File Share
- Email functionality from applications
Customers will have the ability to disable the settings or configure alternate conditional access policies. However, disabling the Security Defaults would create vulnerabilities across your Microsoft accounts leaving your organization’s cybersecurity at risk.
Microsoft released Security Defaults back in 2019 to ensure that basic cybersecurity measures, such as MFA, were being used on their accounts. Because of this, over 30 million organizations already have baseline Security Defaults in place. This has allowed these companies to experience 80% less compromised accounts compared to companies without Security Defaults.
MFA alone is known for being the most effective tool at preventing compromised accounts, yet it is one of the most underutilized security measures. Microsoft’s Security Report states that MFA can block over 99.9% of account compromised attacks.
Databranch has taken the step of proactively enabling these Security Defaults for our own Microsoft tenant. This not only improves the cybersecurity of our Microsoft accounts, but it will also allow us to experience these changes first hand so we can better serve our clients.
We are also performing a review of the Office 365 tenants for all of our managed clients, so that we can proactively get their Security Defaults enabled, if they are not already.
Reach out today at [email protected] or 716-373-4467 if you have questions about these changes or wish to speak with one of our team members about enabling MFA for more accounts.
Read More

Misconfiguration of cloud solutions is often overlooked when companies plan cybersecurity strategies. Cloud apps are typically quick and easy to sign up for, so the user often assumes that they don’t need to worry about security because it’s handled.
This is an incorrect assumption because cloud security is a shared model. The provider of the solution handles securing the backend infrastructure but the user is responsible for configuring security settings in their account properly.
Problems with misconfiguration are the number one cause of cloud data breaches. It’s also an unforced error. Misconfiguration means that a company has made a mistake because it hasn’t adequately secured its cloud application.
Perhaps they gave too many employees administrative privileges or, they may have neglected to turn on a security function that would have prevented the downloading of cloud files by an unauthorized user.
Misconfiguration covers a wide range of negligent behavior. It all has to do with cloud security settings and practices. A finding in The State of Cloud Security 2021 shed light on how common this issue is. Around 45% of organizations experience between 1 and 50 cloud misconfigurations per day.
Some of the main causes of misconfiguration are:
- Lack of adequate oversight and controls
- A team lacking security awareness
- Too many cloud APIs to manage
- No adequate cloud environment monitoring
- Negligent insider behavior
- Not enough expertise in cloud security
Use the tips below to reduce your risk of a cloud data breach and improve cloud security.
Enable Visibility into Your Cloud Infrastructure
Do you know all the different cloud apps employees are using at your business? If not, you’re not alone. It’s estimated that shadow IT use is approximately 10x the size of known cloud use.
When an employee uses a cloud app without authorization, it’s considered “shadow IT.” This is because the app is in the shadows so to speak, outside the purview of the company’s IT team.
How can you protect something you don’t know about? This is why shadow cloud applications are so dangerous and why they often result in breaches due to misconfiguration.
Gain visibility into your entire cloud environment, so you know what you need to protect. One way you can do this is through a cloud access security application.
Restrict Privileged Accounts
The more privileged accounts you have, the higher the risk of a misconfiguration. There should be very few users that can change security configurations. You don’t want someone that doesn’t know better to accidentally open a vulnerability, such as removing a cloud storage sharing restriction. It could leave your entire environment a sitting duck for hackers.
Audit privileged accounts in all cloud tools. Then, reduce the number of administrative accounts to a least needed to operate.
Click here to learn more about the risks associated with Administrative Privileges.
Put in Place Automated Security Policies
Automation helps mitigate human error. Automating as many security policies as possible helps prevent cloud security breaches.
For example, if you use a feature like sensitivity labels in Microsoft 365, you can set a “do not copy” policy. It will follow the file through each supported cloud application. Users don’t need to do anything to enable it once you put the policy in place.
Use a Cloud Security Audit Tool (Like Microsoft Secure Score)
How secure is your cloud environment? How many misconfigurations might there be right now? It’s important to know this information so you can correct issues to reduce risk.
Use an auditing tool, like Microsoft Secure Score. You want a tool that can scan your cloud environment and let you know where problems exist. It should also be able to provide recommended remediation steps.
Set Up Alerts for When Configurations Change
Once you get your cloud security settings right, they won’t necessarily stay that way. Several things can cause a change in a security setting without you realizing it. These include:
- An employee with elevated permissions accidentally changes them
- A change caused by an integrated 3rd party plug-in
- Software updates
- A hacker that has compromised a privileged user credential
Be proactive by setting up alerts. You should have an alert for any significant change in your cloud environment. For example, when the setting to force multi-factor authentication gets turned off.
If an alert is set up, then your team knows right away when a change occurs to an important security setting. This allows them to take immediate steps to research and rectify the situation.
Have a Cloud Specialist Check Your Cloud Settings
Business owners, executives, and office managers usually are not cybersecurity experts and no one should expect them to know how to configure the best security for your organization’s needs.
It’s best to have a cloud security specialist from Databranch check your settings. Thinking about moving your applications from your local server to the cloud? We can help ensure that they’re set up to keep your data protected without restricting your team.
Improve Cloud Security & Lower Your Chances for a Data Breach
Most work is now done in the cloud, and companies store data in these online environments. Don’t leave your company at risk by neglecting to review your cloud security configuration. Contact Databranch today at 716-373-4467 x 115 or [email protected] to set up a cloud security assessment.
Article used with permission from The Technology Press.
Read More

Databranch has been tracking a Microsoft Outlook security flaw, CVE-2023-23397.
The critical Outlook exploit affects both 32 and 64-bit versions of Microsoft 365 Apps for Enterprise. Office 2013, 2016, and 2019.
It is triggered by sending a malicious email (which doesn’t even need to be opened) that lets attackers capture the Net-NTLMv2 hash (challenge response protocols used for authentication in Windows environments) of the recipient and thereby authenticate as the victim.
More information can be found here.
Microsoft has released a patch to address some instances of Outlook.
If you are a managed maintenance client, we are actively working to patch vulnerable instances of Outlook for you.
You may see the following prompts as your client is updated.
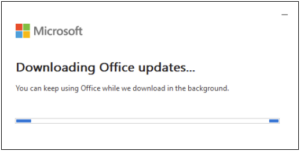
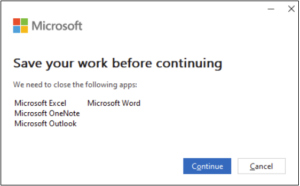
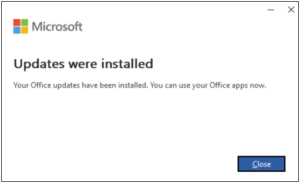
Please feel free to reach out to [email protected] with any questions.
If you are not a managed client and would like to discuss how Databranch can help to proactively manage, monitor, and patch your IT environment, please reach out to Databranch at 716-373-4467 x115 or [email protected].
Read More

No business wants to suffer a data breach. But unfortunately, in today’s environment, it’s difficult to completely avoid them. Approximately 83% of organizations have experienced more than one data breach. (IBM Security 2022 Cost of a Data Breach Report)
These breaches hurt businesses in many ways. First, there is the immediate cost of remediating the breach. Then, there are the lost productivity costs. You can add lost business on top of that along with lost customer trust. A business could also have extensive legal costs associated with a breach.
Visit our website here to see what the cost of downtime would be for your business.
According to IBM Security’s report, the cost of a data breach climbed again in 2022. The global cost of one breach is now $4.35 million, up 2.6% from last year. If your business is in the U.S., the cost rises to $9.44 million. In Canada, the average data breach costs companies $5.64 million.
Costs for smaller companies tend to be a little lower. But breaches are often more devastating to SMBs. They don’t have the same resources that larger companies do to offset all those costs.
It’s estimated that 60% of small companies go out of business within six months of a cybersecurity breach.
Companies don’t need to resign themselves to the impending doom of a data breach. There are some proven tactics they can take to mitigate the costs. These cybersecurity practices can limit the damage of a cyberattack.
All these findings come from the IBM Security report. They include hard facts on the benefits of bolstering your cybersecurity strategy.
Cybersecurity Tactics to Reduce the Impact of a Breach
Use a Hybrid Cloud Approach
Most organizations use the cloud for data storage and business processes. Researchers found that 45% of all data breaches happen in the cloud. But all cloud strategies are not created equally.
Breaches in the public cloud cost significantly more than those in a hybrid cloud. What is a hybrid cloud? It means that some data and processes are in a public cloud, and some are in a private cloud environment.
What some may find surprising is that using a hybrid cloud approach was also better than a private cloud.
Put in Place a Disaster Recovery Plan & Practice It
You don’t need to be a large enterprise to create an Disaster Recovery (DR) plan. The DR plan is a set of instructions for employees to follow should any number of cybersecurity incidents occur.
Along with this, it is the Business Continuity Solution put in place by the business to monitor backup processes, implement recovery objectives and restore your data to its former state.
Here is an example. In the case of ransomware, the first step should be disconnecting the infected device. DR plans improve the speed and effectiveness of a response in the face of a security crisis.
Having a practiced Disaster Recovery plan reduces the cost of a data breach by an average of $2.66 million per incident.
Need help setting up your Disaster Recovery plan? We’re ready to help you with a custom-built business continuity solution that meets the needs of your unique business. Give our experts a call at 716-373-4467 x115 or click here to get started.
Adopt a Zero Trust Security Approach
Zero trust is a collection of security protocols that work together to fortify a network. An example of a few of these are:
Approximately 79% of critical infrastructure organizations haven’t adopted zero trust. Doing so can significantly reduce data breach costs. Organizations that don’t deploy zero trust tactics pay about $1 million more per data breach.
Use Tools with Security AI & Automation
Using the right security tools can make a big difference in the cost incurred during a data breach. Using tools that deploy security AI and automation brought the biggest cost savings.
Data breach expense lowered by 65.2% thanks to security AI and automation solutions. These types of solutions include tools like advanced threat protection (ATP). They can also include applications that hunt out threats and automate the response.
Here at Databranch, we use a number of automated remote monitoring tools that will inspect your system 24/7, 365 days a year to help prevent attacks from happening to your organization. Click here to learn more.
How to Get Started Improving Your Cyber Resilience
Many of these ways to lower data breach costs are simply best practices. You can get started by taking them one at a time and rolling out upgrades to your cybersecurity strategy.
Databranch will even help you put together a roadmap to achieve this in the most efficient way possible. Address the “low-hanging fruit” first. Then, move on to longer-term projects.
As an example, “low-hanging fruit” would be putting multi-factor authentication in place. It’s low-cost and easy to put in place. It also significantly reduces the risk of a cloud breach.
A longer-term project might be creating an incident response plan. Then, you would set up a schedule to have your team drill on the plan regularly. During those drills, you could work out any kinks.
Need Help Improving Your Security & Reducing Risk?
Working with Databranch can take the cybersecurity burden off your shoulders. Contact us today at 716-373-4467 x 115 or [email protected] to discuss your security needs.
Article used with permission from The Technology Press.
Read More

Imagine you’re going about your day when suddenly you receive a text from the CEO asking for your help. They’re out doing customer visits and someone else dropped the ball in providing gift cards. The CEO needs you to buy six $200 gift cards and text the information right away.
The message sender promises to reimburse you before the end of the day. Oh, and by the way, you won’t be able to reach them by phone for the next two hours because they’ll be in meetings. One last thing, this is a high priority. They need those gift cards urgently.
Would this kind of request make you pause and wonder or would you quickly pull out your credit card to do as the message asked?
A surprising number of employees fall for this gift card scam. There are also many variations. Such as your boss being stuck without gas or some other dire situation that only you can help with.
This scam can come by text message or via email. The unsuspecting employee buys the gift cards and sends the numbers back to the boss. They find out later that the real company CEO wasn’t the one that contacted them, it was a phishing scammer.
The employee is out the cash.
Without proper training, 32.4% of employees are prone to fall for a phishing scam.
Read about our Employee Security Awareness training and the services it offers here.
Why Do Employees Fall for Phishing Scams?
Though the circumstances may be odd, many employees fall for this gift card scam. Hackers use social engineering tactics and manipulate emotions to get the employee to follow through on the request.
Some of these social engineering tactics illicit the following:
- The employee is afraid of not doing as asked by a superior
- The employee jumps at the chance to save the day
- The employee doesn’t want to let their company down
- The employee may feel they can advance in their career by helping
The scam’s message is also crafted in a way to get the employee to act without thinking or checking. It includes a sense of urgency. The CEO needs the gift card details right away. Also, the message notes that the CEO will be out of touch for the next few hours. This decreases the chance the employee will try to contact the real CEO to check the validity of the text.
Illinois Woman Scammed Out of More Than $6,000 from a Fake CEO Email
Variations of this scam are prevalent and can lead to significant financial losses. A company isn’t responsible if an employee falls for a scam and purchases gift cards with their own money.
In one example, a woman from Palos Hills, Illinois lost over $6,000. This was after getting an email request from who she thought was her company’s CEO.
The woman received an email purporting to be from her boss and company CEO. It stated that her boss wanted to send gift cards to some selected staff that had gone above and beyond.
The email ended with “Can you help me purchase some gift cards today?” The boss had a reputation for being great to employees, so the email did not seem out of character.
The woman bought the requested gift cards from Target and Best Buy. Then she got another request asking to send a photo of the cards. Again, the wording in the message was very believable and non-threatening. It simply stated, “Can you take a picture, I’m putting this all on a spreadsheet.”
The woman ended up purchasing over $6,500 in gift cards that the scammer then stole. When she saw her boss a little while later, her boss knew nothing about the gift card request. The woman realized she was the victim of a scam.
Tips for Avoiding Costly Phishing Scams
Always Double Check Unusual Requests
Despite what a message might say about being unreachable, check in person or by phone anyhow. If you receive any unusual requests or one relating to money, verify it. Contact the person through other means to make sure it’s legitimate.
Databranch recommends using the SLAM Method to review your emails and act accordingly. Don’t know what the SLAM Method is? Click here to read all about it.
Don’t React Emotionally
Scammers often try to get victims to act before they have time to think. Just a few minutes of sitting back and looking at a message objectively is often all that’s needed to realize it’s a scam. Don’t react emotionally, instead ask if this seems real or is it out of the ordinary.
Get a Second Opinion
Ask a colleague, or better yet, your company’s IT service provider, to take look at the message. Getting a second opinion keeps you from reacting right away. It can save you from making a costly judgment error.
Need Help with Employee Phishing Awareness Training?
Phishing keeps getting more sophisticated all the time, are your employee’s up to date on their security awareness training?
Take training off your plate and train your team with cybersecurity professionals. We can help you with an engaging training program that helps your team change their behaviors to improve cyber hygiene.
Contact Databranch today at 716-373-4467 x 115 or [email protected] if you would like to learn more about our Breach Prevention Platform and Security Awareness Training with simulated phishing tests.
Article used with permission from The Technology Press.
Read More


















